- Research Article
- Open access
- Published:
Three Solutions to Dirichlet Boundary Value Problems for  -Laplacian Difference Equations
-Laplacian Difference Equations
Advances in Difference Equations volume 2008, Article number: 345916 (2007)
Abstract
We deal with Dirichlet boundary value problems for  -Laplacian difference equations depending on a parameter
-Laplacian difference equations depending on a parameter  . Under some assumptions, we verify the existence of at least three solutions when
. Under some assumptions, we verify the existence of at least three solutions when  lies in two exactly determined open intervals respectively. Moreover, the norms of these solutions are uniformly bounded in respect to
lies in two exactly determined open intervals respectively. Moreover, the norms of these solutions are uniformly bounded in respect to  belonging to one of the two open intervals.
belonging to one of the two open intervals.
1. Introduction
Let  be all real numbers, integers, and positive integers, respectively. Denote
be all real numbers, integers, and positive integers, respectively. Denote  and
and  with
with  for any
for any  .
.
In this paper, we consider the following discrete Dirichlet boundary value problems:

where  is a positive integer,
is a positive integer,  is a constant,
is a constant,  is the forward difference operator defined by
is the forward difference operator defined by  ,
,  is a
is a  -Laplacian operator, that is,
-Laplacian operator, that is,  ,
,  for any
for any  .
.
There seems to be increasing interest in the existence of solutions to boundary value problems for finite difference equations with  -Laplacian operator, because of their applications in many fields. Results on this topic are usually achieved by using various fixed point theorems in cone; see [1–4] and references therein for details. It is well known that critical point theory is an important tool to deal with the problems for differential equations. In the last years, a few authors have gradually paid more attentions to applying critical point theory to deal with problems for nonlinear second discrete systems; we refer to [5–9]. But all these systems do not concern with the
-Laplacian operator, because of their applications in many fields. Results on this topic are usually achieved by using various fixed point theorems in cone; see [1–4] and references therein for details. It is well known that critical point theory is an important tool to deal with the problems for differential equations. In the last years, a few authors have gradually paid more attentions to applying critical point theory to deal with problems for nonlinear second discrete systems; we refer to [5–9]. But all these systems do not concern with the  -Laplacian. For the reader's convenience, we recall the definition of the weak closure.
-Laplacian. For the reader's convenience, we recall the definition of the weak closure.
Suppose that  . We denote
. We denote  as the weak closure of
as the weak closure of  , that is,
, that is,  if there exists a sequence
if there exists a sequence  such that
such that  for every
for every  .
.
Very recently, based on a new variational principle of Ricceri [10], the following three critical points was established by Bonanno [11].
Theorem(see 1.1 (see {[11, Theorem 2.1]}).
Let  be a separable and reflexive real Banach space.
be a separable and reflexive real Banach space.  a nonnegative continuously Gâteaux differentiable and sequentially weakly lower semicontinuous functional whose Gâteaux derivative admits a continuous inverse on
a nonnegative continuously Gâteaux differentiable and sequentially weakly lower semicontinuous functional whose Gâteaux derivative admits a continuous inverse on  .
.  a continuously Gâteaux differentiable functional whose Gâteaux derivative is compact. Assume that there exists
a continuously Gâteaux differentiable functional whose Gâteaux derivative is compact. Assume that there exists  such that
such that  and that
and that
-
(i)
 for all
for all 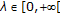 ;
;Further, assume that there are
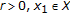 such that
such that -
(ii)
 ;
; -
(iii)
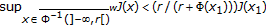 .
.Then, for each
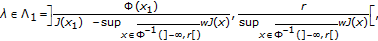 (1.2)
(1.2)
the equation

has at least three solutions in  and, moreover, for each
and, moreover, for each  , there exists an open interval
, there exists an open interval

and a positive real number  such that, for each
such that, for each  , (1.3) has at least three solutions in
, (1.3) has at least three solutions in  whose norms are less than
whose norms are less than  .
.
Here, our principle aim is by employing Theorem 1.1 to establish the existence of at least three solutions for the  -Laplacian discrete boundary value problem (1.1).
-Laplacian discrete boundary value problem (1.1).
The paper is organized as follows. The next section is devoted to give some basic definitions. In Section 3, under suitable hypotheses, we prove that the problem (1.1) possesses at least three solutions when  lies in exactly determined two open intervals, respectively; moreover, all these solutions are uniformly bounded with respect to
lies in exactly determined two open intervals, respectively; moreover, all these solutions are uniformly bounded with respect to  belonging to one of the two open intervals. At last, a consequence is presented.
belonging to one of the two open intervals. At last, a consequence is presented.
2. Preliminaries
The class  of the functions
of the functions  such that
such that  is a
is a  -dimensional Hilbert space with inner product
-dimensional Hilbert space with inner product

We denote the induced norm by

Furthermore, for any constant  , we define other norms
, we define other norms

Since  is a finite dimensional space, there exist constants
is a finite dimensional space, there exist constants  such that
such that

The following two functionals will be used later:

where  ,
,  for any
for any  . Obviously,
. Obviously,  , that is,
, that is,  and
and  are continuously Fréchet differentiable in
are continuously Fréchet differentiable in  . Using the summation by parts formula and the fact that
. Using the summation by parts formula and the fact that  for any
for any  , we get
, we get

for any  . Noticing the fact that
. Noticing the fact that  for any
for any  again, we obtain
again, we obtain

for any  .
.
Remark 2.1.
Obviously, for any  ,
,

is equivalent to

for any  with
with  . That is, a critical point of the functional
. That is, a critical point of the functional  corresponds to a solution of the problem (1.1). Thus, we reduce the existence of a solution for the problem (1.1) to the existence of a critical point of
corresponds to a solution of the problem (1.1). Thus, we reduce the existence of a solution for the problem (1.1) to the existence of a critical point of  on
on  .
.
The following estimate will play a key role in the proof of our main results.
Lemma 2.2.
For any  and
and  , the relation
, the relation

holds.
Proof.
Let  such that
such that

Since  for any
for any  , by Cauchy-Schwarz inequality, we get
, by Cauchy-Schwarz inequality, we get


for any  , where
, where  is the conjugative number of
is the conjugative number of  , that is,
, that is,  .
.
If

jointly with the estimate (2.12), we get the required relation (2.10).
If, on the contrary,

thus,

Combining the above inequality with the estimate (2.13), we have

Now, we claim that the inequality

holds, which leads to the required inequality (2.10). In fact, we define a continuous function  by
by

This function  can attain its minimum
can attain its minimum  at
at  . Since
. Since  , we have
, we have  , namely,
, namely,

This implies the assertion (2.18). Lemma 2.2 is proved.
3. Main Results
First, we present our main results as follows.
Theorem 3.1.
Let  for any
for any  . Put
. Put  for any
for any  and assume that there exist four positive constants
and assume that there exist four positive constants  with
with  and
and  such that
such that
(A1) 
(A2)  .
.
Furthermore, put

and for each  ,
,

Then, for each

the problem (1.1) admits at least three solutions in  and, moreover, for each
and, moreover, for each  , there exist an open interval
, there exist an open interval  and a positive real number
and a positive real number  such that, for each
such that, for each  , the problem (1.1) admits at least three solutions in
, the problem (1.1) admits at least three solutions in  whose norms in
whose norms in  are less than
are less than  .
.
Remark 3.2.
By the condition (A1), we have

That is,

Thus, we get

Namely, we obtain the fact that  .
.
Proof of Theorem 3.1.
Let  be the Hilbert space
be the Hilbert space  . Thanks to Remark 2.1, we can apply Theorem 1.1 to the two functionals
. Thanks to Remark 2.1, we can apply Theorem 1.1 to the two functionals  and
and  . We know from the definitions in (2.5) that
. We know from the definitions in (2.5) that  is a nonnegative continuously Gâteaux differentiable and sequentially weakly lower semicontinuous functional whose Gâteaux derivative admits a continuous inverse on
is a nonnegative continuously Gâteaux differentiable and sequentially weakly lower semicontinuous functional whose Gâteaux derivative admits a continuous inverse on  , and
, and  is a continuously Gâteaux differentiable functional whose Gâteaux derivative is compact. Now, put
is a continuously Gâteaux differentiable functional whose Gâteaux derivative is compact. Now, put  for any
for any  , it is easy to see that
, it is easy to see that  and
and  .
.
Next, in view of the assumption (A2) and the relation (2.4), we know that for any  and
and  ,
,

Taking into account the fact that  , we obtain, for all
, we obtain, for all  ,
,

The condition (i) of Theorem 1.1 is satisfied.
Now, we let

It is clear that  ,
,

In view of  , we get
, we get

So, the assumption (ii) of Theorem 1.1 is obtained. Next, we verify that the assumption (iii) of Theorem 1.1 holds. From Lemma 2.2, the estimate  implies that
implies that

for any  . From the definition of
. From the definition of  , it follows that
, it follows that

Thus, for any  , we have
, we have

On the other hand, we get

Therefore, it follows from the assumption (A1) that

that is, the condition (iii) of Theorem 1.1 is satisfied.
Note that

By a simple computation, it follows from the condition (A1) that  . Applying Theorem 1.1, for each
. Applying Theorem 1.1, for each  , the problem (1.1) admits at least three solutions in
, the problem (1.1) admits at least three solutions in  .
.
For each  , we easily see that
, we easily see that

Taking the condition (A1) into account, it forces that  . Then from Theorem 1.1, for each
. Then from Theorem 1.1, for each  , there exist an open interval
, there exist an open interval  and a positive real number
and a positive real number  , such that, for
, such that, for  , the problem (1.1) admits at least three solutions in
, the problem (1.1) admits at least three solutions in  whose norms in
whose norms in  are less than
are less than  . The proof of Theorem 3.1is complete.
. The proof of Theorem 3.1is complete.
As a special case of the problem (1.1), we consider the following systems:

where  and
and  are nonnegative. Define
are nonnegative. Define

Then Theorem 3.1 takes the following simple form.
Corollary 3.3.
Let  and
and  be two nonnegative functions. Assume that there exist four positive constants
be two nonnegative functions. Assume that there exist four positive constants  with
with  and
and  such that
such that
(A′1) 
(A′2)  for any
for any  .
.
Furthermore, put

and for each  ,
,

Then, for each

the problem (3.19) admits at least three solutions in  and, moreover, for each
and, moreover, for each  , there exist an open interval
, there exist an open interval  and a positive real number
and a positive real number  such that, for each
such that, for each  , the problem (3.19) admits at least three solutions in
, the problem (3.19) admits at least three solutions in  whose norms in
whose norms in  are less than
are less than  .
.
Proof.
Note that from fact  for any
for any  , we have
, we have

On the other hand, we take  . Obviously, all assumptions of Theorem 3.1 are satisfied.
. Obviously, all assumptions of Theorem 3.1 are satisfied.
To the end of this paper, we give an example to illustrate our main results.
Example 3.4.
We consider (1.1) with  , where
, where

We have that  and
and

It can be easily shown that, when  , and
, and  , all conditions of Corollary 3.3 are satisfied.
, all conditions of Corollary 3.3 are satisfied.
References
Avery R, Henderson J:Existence of three positive pseudo-symmetric solutions for a one dimensional discrete
 -Laplacian. Journal of Difference Equations and Applications 2004, 10(6):529-539. 10.1080/10236190410001667959
-Laplacian. Journal of Difference Equations and Applications 2004, 10(6):529-539. 10.1080/10236190410001667959He Z:On the existence of positive solutions of
 -Laplacian difference equations. Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics 2003, 161(1):193-201. 10.1016/j.cam.2003.08.004
-Laplacian difference equations. Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics 2003, 161(1):193-201. 10.1016/j.cam.2003.08.004Li Y, Lu L:Existence of positive solutions of
 -Laplacian difference equations. Applied Mathematics Letters 2006, 19(10):1019-1023. 10.1016/j.aml.2005.10.020
-Laplacian difference equations. Applied Mathematics Letters 2006, 19(10):1019-1023. 10.1016/j.aml.2005.10.020Liu Y, Ge W:Twin positive solutions of boundary value problems for finite difference equations with
 -Laplacian operator. Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications 2003, 278(2):551-561. 10.1016/S0022-247X(03)00018-0
-Laplacian operator. Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications 2003, 278(2):551-561. 10.1016/S0022-247X(03)00018-0Agarwal RP, Perera K, O'Regan D: Multiple positive solutions of singular and nonsingular discrete problems via variational methods. Nonlinear Analysis: Theory, Methods & Applications 2004, 58(1-2):69-73. 10.1016/j.na.2003.11.012
Guo ZM, Yu JS: Existence of periodic solutions and subharmonic solutions on second order superlinear difference equations. Science in China Series A 2003, 33(3):226-235.
Jiang L, Zhou Z: Existence of nontrivial solutions for discrete nonlinear two point boundary value problems. Applied Mathematics and Computation 2006, 180(1):318-329. 10.1016/j.amc.2005.12.018
Zhou Z, Yu J, Guo Z: Periodic solutions of higher-dimensional discrete systems. Proceedings of the Royal Society of Edinburgh: Section A 2004, 134(5):1013-1022. 10.1017/S0308210500003607
Zhou Z, Yu J, Guo Z: The existence of periodic and subharmonic solutions to subquadratic discrete Hamiltonian systems. The ANZIAM Journal 2005, 47(1):89-102. 10.1017/S1446181100009792
Ricceri B: On a three critical points theorem. Archiv der Mathematik 2000, 75(3):220-226. 10.1007/s000130050496
Bonanno G: A critical points theorem and nonlinear differential problems. Journal of Global Optimization 2004, 28(3-4):249-258.
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 10571032) and Doctor Scientific Research Fund of Jishou university (no. jsdxskyzz200704).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 2.0 International License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, L., Zhou, Z. Three Solutions to Dirichlet Boundary Value Problems for  -Laplacian Difference Equations.
Adv Differ Equ 2008, 345916 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1155/2008/345916
-Laplacian Difference Equations.
Adv Differ Equ 2008, 345916 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1155/2008/345916
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2008/345916
 for all
for all 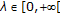 ;
;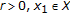 such that
such that ;
;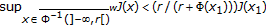 .
.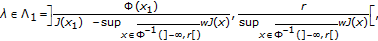
 -Laplacian. Journal of Difference Equations and Applications 2004, 10(6):529-539. 10.1080/10236190410001667959
-Laplacian. Journal of Difference Equations and Applications 2004, 10(6):529-539. 10.1080/10236190410001667959 -Laplacian difference equations. Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics 2003, 161(1):193-201. 10.1016/j.cam.2003.08.004
-Laplacian difference equations. Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics 2003, 161(1):193-201. 10.1016/j.cam.2003.08.004 -Laplacian difference equations. Applied Mathematics Letters 2006, 19(10):1019-1023. 10.1016/j.aml.2005.10.020
-Laplacian difference equations. Applied Mathematics Letters 2006, 19(10):1019-1023. 10.1016/j.aml.2005.10.020 -Laplacian operator. Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications 2003, 278(2):551-561. 10.1016/S0022-247X(03)00018-0
-Laplacian operator. Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications 2003, 278(2):551-561. 10.1016/S0022-247X(03)00018-0