- Research Article
- Open access
- Published:
Multiple Positive Solutions of  -Point BVPs for Third-Order
-Point BVPs for Third-Order 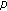 -Laplacian Dynamic Equations on Time Scales
-Laplacian Dynamic Equations on Time Scales
Advances in Difference Equations volume 2009, Article number: 262857 (2009)
Abstract
This paper is concerned with the existence of multiple positive solutions for the third-order  -Laplacian dynamic equation
-Laplacian dynamic equation  with the multipoint boundary conditions
with the multipoint boundary conditions  , where
, where  with
with  . Using the fixed point theorem due to Avery and Peterson, we establish the existence criteria of at least three positive solutions to the problem. As an application, an example is given to illustrate the result. The interesting points are that not only do we consider third-order
. Using the fixed point theorem due to Avery and Peterson, we establish the existence criteria of at least three positive solutions to the problem. As an application, an example is given to illustrate the result. The interesting points are that not only do we consider third-order  -Laplacian dynamic equation but also the nonlinear term
-Laplacian dynamic equation but also the nonlinear term  is involved with the first-order delta derivative of the unknown function.
is involved with the first-order delta derivative of the unknown function.
1. Introduction
The theory of dynamic equations on time scales was introduced by Stefan Hilger in 1988 [1]. This theory has attracted many researchers' attention and interest since it cannot only unify differential and difference equations but also provides accurate information of phenomena that manifest themselves partly in continuous time and partly in discrete time. In addition, time-scale calculus would allow exploration of a variety of situations in economic, biological, heat transfer, stock market, and epidemic models [2, 3], and so forth.
Recently, there has been much attention paid to the existence of positive solutions for second-order nonlinear boundary value problems on time scales; see [4–10] and the references therein. On the one hand, higher-order nonlinear boundary value problems have been studied extensively; see [11–14] and the references therein. On the other hand, the boundary value problems with  -Laplacian operator have also been discussed extensively in literature; for example, see [15–17]. However, very little work has been done to the third-order
-Laplacian operator have also been discussed extensively in literature; for example, see [15–17]. However, very little work has been done to the third-order  -Laplacian dynamic equations on time scales [18, 19].
-Laplacian dynamic equations on time scales [18, 19].
For convenience, throughout this paper, we denote  as
as  -Laplacian operator, that is,
-Laplacian operator, that is,  for
for  with
with  and
and  We also assume that
We also assume that  is a closed subset of
is a closed subset of  with
with  ; an interval
; an interval  always means
always means  . Other types of intervals are defined similarly.
. Other types of intervals are defined similarly.
For example, Sun and Li [16] studied the two-point boundary value problem:

They established the existence theory for positive solutions by using various fixed point theorems [20, 21].
In [15], Su et al. investigated the existence of positive solutions for the following singular  -Laplacian
-Laplacian  -point boundary value problem on time scales:
-point boundary value problem on time scales:

The main techniques are Schauder fixed point theorem and upper and lower solutions method.
In [19], Han and Kang considered the following third-order  -Laplacian dynamic equation on time scales:
-Laplacian dynamic equation on time scales:

By using fixed point theorems in cones, the existence criteria of multiple positive solutions are established.
In [10], Zhao and Sun studied the following second-order nonlinear three-point boundary value problem on time scales:

They gave sufficient condition for the existence of three positive solutions by using a fixed point theorem due to Avery and Peterson [22].
Motivated by [10, 15, 16, 19], in this paper we consider the following third-order  -Laplacian dynamic equation on time scales:
-Laplacian dynamic equation on time scales:

subject to the boundary condition

where  ,
,  for
for  . By using fixed point theorem due to Avery and Peterson [22], we prove that the boundary value problems (1.5) and (1.6) have at least three positive solutions under suitable assumptions. The interesting points are that not only do we consider third-order
. By using fixed point theorem due to Avery and Peterson [22], we prove that the boundary value problems (1.5) and (1.6) have at least three positive solutions under suitable assumptions. The interesting points are that not only do we consider third-order  -Laplacian dynamic equation on time scales but also the nonlinear term
-Laplacian dynamic equation on time scales but also the nonlinear term  is involved with the first-order delta derivative of the unknown function.
is involved with the first-order delta derivative of the unknown function.
Throughout this paper, it is assumed that
-
(H1)
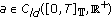 and
and 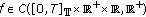 , both
, both  and
and 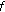 do not vanish identically on any closed subinterval of
do not vanish identically on any closed subinterval of  , and there exists
, and there exists 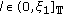 such that
such that 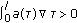 hold;
hold; -
(H2)
there exist nonnegative constants
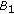 and
and 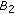 satisfying
satisfying  for
for 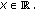
2. Preliminary
To prove the main results in this paper, we will employ several lemmas. And the following lemma is based on the linear BVP:


Lemma 2.1.
If  , then the problems (2.1) and (2.2) have the unique nonnegative solution:
, then the problems (2.1) and (2.2) have the unique nonnegative solution:

Proof.
For any  , suppose that
, suppose that  is a solution of the BVPs (2.1) and (2.2). By integrating (2.1) from
is a solution of the BVPs (2.1) and (2.2). By integrating (2.1) from  to
to  , and combining the boundary condition, it follows that
, and combining the boundary condition, it follows that

Using (2.2), we can easily obtain

So

Then it is easy to see that

So  . On the other hand, it is easy to verify that if
. On the other hand, it is easy to verify that if  is as in (2.3), then
is as in (2.3), then  is a solution of (2.1) and (2.2). Thus
is a solution of (2.1) and (2.2). Thus  in (2.3) is the unique solution of (2.1) and (2.2).
in (2.3) is the unique solution of (2.1) and (2.2).
Let  =
=  be endowed with the norm
be endowed with the norm

It follows that  is a Banach space. Define the cone
is a Banach space. Define the cone  by
by

Lemma 2.2.
If  , then there exists a constant
, then there exists a constant  such that
such that

Proof.
For  ,
,  implies that
implies that

In addition, since

then we have

Therefore, We can choose  and the proof is complete.
and the proof is complete.
Lemma 2.3.
If  , then
, then  for
for  .
.
Proof.
If  , then
, then  is decreasing and
is decreasing and  , and thus
, and thus  and
and  are decreasing. So we have
are decreasing. So we have

By the concavity of  , for
, for  , there is
, there is

Then we have

The proof is complete.
Let  and
and  be nonnegative continuous convex functionals on
be nonnegative continuous convex functionals on  , let
, let  be a nonnegative continuous concave functional on
be a nonnegative continuous concave functional on  , and let
, and let  be a nonnegative continuous functional on
be a nonnegative continuous functional on  . Then for positive real numbers
. Then for positive real numbers  and
and  , we define the following convex sets:
, we define the following convex sets:

and a closed set

The following fixed point theorem due to Avery and Peterson is fundamental in the proof of our main results.
Lemma 2.4 (see [22]).
Let  be a cone in a real Banach space
be a cone in a real Banach space  . Let
. Let  and
and  be nonnegative continuous convex functionals on
be nonnegative continuous convex functionals on  , let
, let  be a nonnegative continuous concave functional on
be a nonnegative continuous concave functional on  , and let
, and let  be a nonnegative continuous functional on
be a nonnegative continuous functional on  satisfying
satisfying  for
for  , such that for some positive numbers
, such that for some positive numbers  and
and  ,
,

for all  . Suppose that
. Suppose that  is completely continuous and there exist positive numbers
is completely continuous and there exist positive numbers  , and
, and  with
with  such that
such that
-
(S1)
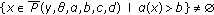 and
and 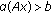 for
for  ;
; -
(S2)
 for
for 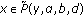 with
with 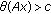 ;
; -
(S3)
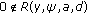 and
and  for
for 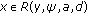 with
with 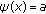 .
.
Then  has at least three fixed points
has at least three fixed points  , such that
, such that

3. Existence Results
In this section, by using the Avery-Peterson fixed point theorem, we shall give the sufficient conditions for the existence of at least three positive solutions to the BVPs (1.5) and (1.6).
Firstly, we define the nonnegative continuous concave functional  , the nonnegative continuous convex functionals
, the nonnegative continuous convex functionals  , and the nonnegative continuous functional
, and the nonnegative continuous functional  on
on  , respectively, by
, respectively, by

For notation convenience, we denote

Now we state and prove our main result.
Theorem 3.1.
Let  and suppose that
and suppose that  satisfies the following conditions:
satisfies the following conditions:
-
(A1)
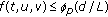 for
for 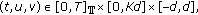
-
(A2)
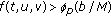 for
for 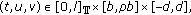
-
(A3)
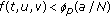 for
for 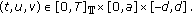
Then problems (1.5) and (1.6) have at least three positive solutions  , and
, and  such that
such that

Proof.
Define an integral operator  by
by

for  . It is easy to obtain that
. It is easy to obtain that  is a completely continuous operator and every fixed point of
is a completely continuous operator and every fixed point of  is a solution of (1.5) and (1.6).
is a solution of (1.5) and (1.6).
Thus we set out to verify that the operator  satisfies Avery-Peterson fixed point theorem which will prove the existence of three fixed points of
satisfies Avery-Peterson fixed point theorem which will prove the existence of three fixed points of  . Now the proof is divided into some steps.
. Now the proof is divided into some steps.
By virtue of  ,
,  ,
,  and Lemma 2.2 we know that there exists a constant
and Lemma 2.2 we know that there exists a constant  such that
such that

We first show that  implies that
implies that

In fact, for  ,
,  , by Lemma 2.2, there is
, by Lemma 2.2, there is  It follows from
It follows from  that
that

Thus (3.6) holds.
Next we show that condition  in Lemma 2.4 holds. Let
in Lemma 2.4 holds. Let  Then it is easy to see that
Then it is easy to see that  ,
,  , and
, and  for
for  , so
, so  . Also, we have
. Also, we have

So  . Hence
. Hence 
If  , then
, then  for
for  It follows from condition
It follows from condition  that
that

Therefore we have

That is, condition  in Lemma 2.4 is satisfied.
in Lemma 2.4 is satisfied.
We now prove that  in Lemma 2.4 holds. In fact, since
in Lemma 2.4 holds. In fact, since  then with Lemma 2.3 it follows that
then with Lemma 2.3 it follows that

for  with
with  . Hence condition
. Hence condition  in Lemma 2.4 is satisfied.
in Lemma 2.4 is satisfied.
Finally, we assert that  in Lemma 2.4 also holds.
in Lemma 2.4 also holds.
Observe that  , so
, so  Suppose
Suppose  with
with  Then, by hypothesis
Then, by hypothesis  we have
we have

Thus condition  in Lemma 2.4 holds.
in Lemma 2.4 holds.
Therefore an application of Lemma 2.4 implies that the BVPs (1.5) and (1.6) have at least three positive solutions  , and
, and  such that (3.3) holds.
such that (3.3) holds.
4. Example
In this section, we present an example to explain our result.
Let  ,
,  ,
,  , and
, and  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  . We consider the following boundary value problem:
. We consider the following boundary value problem:

where

Choosing  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  , direct calculation shows that
, direct calculation shows that

Consequently,  satisfies
satisfies
-
(i)
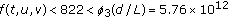 for
for 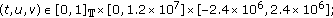
-
(ii)
 for
for 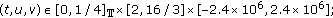
-
(iii)
 for
for 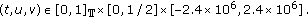
Then all conditions of Theorem 3.1 hold. Thus with Theorem 3.1, the BVP (4.1) has at least three positive solutions  ,
,  , and
, and  such that
such that

References
Hilger S: Ein Maßkettenkalkül mit Anwendung auf Zentrumsmannigfaltigkeiten, Ph.D. thesis. Universität Würzburg, Würzburg, Germany; 1988.
Spedding V: Taming nature's numbers. New Scientist July 2003, 28–32.
Thomas DM, Vandemuelebroeke L, Yamaguchi K: A mathematical evolution model for phytoremediation of metals. Discrete and Continuous Dynamical Systems B 2005,5(2):411–422.
Agarwal RP, Espinar VO, Perera K, Vivero DR: Multiple positive solutions in the sense of distributions of singular BVPs on time scales and an application to Emden-Fowler equations. Advances in Difference Equations 2008, 2008:-13.
Agarwal RP, Espinar VO, Perera K, Vivero DR: Multiple positive solutions of singular Dirichlet problems on time scales via variational methods. Nonlinear Analysis: Theory, Methods & Applications 2007,67(2):368–381. 10.1016/j.na.2006.05.014
Bohner M, Peterson A: Dynamic Equations on Time Scales. Birkhäuser, Boston, Mass, USA; 2001:x+358.
Bohner M, Peterson A: Advances in Dynamic Equations on Time Scales. Birkhäuser, Boston, Mass, USA; 2003:xii+348.
Li WT, Sun HR: Positive solutions for second-order -point boundary value problems on time scales. Acta Mathematica Sinica 2006,22(6):1797–1804. 10.1007/s10114-005-0748-5
Wang Y, Ge W: Positive solutions for multipoint boundary value problems with a one-dimensional -Laplacian. Nonlinear Analysis: Theory, Methods & Applications 2007,66(6):1246–1256. 10.1016/j.na.2006.01.015
Zhao B, Sun HR: Multiplicity results of positive solution for nonlinear three-point boundary value problem on time scales. Advances in Dynamical Systems and Applications 2009,4(2):25–43.
Henderson J: Multiple solutions for -th order Sturm-Liouville boundary value problems on a measure chain. Journal of Difference Equations and Applications 2000,6(4):417–429. 10.1080/10236190008808238
Li SH: Positive solutions of nonlinear singular third-order two-point boundary value problem. Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications 2006,323(1):413–425. 10.1016/j.jmaa.2005.10.037
Sun YP: Positive solutions of singular third-order three-point boundary value problem. Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications 2005,306(2):589–603. 10.1016/j.jmaa.2004.10.029
Yaslan İ: Existence results for an even-order boundary value problem on time scales. Nonlinear Analysis: Theory, Methods & Applications 2009,70(1):483–491. 10.1016/j.na.2007.12.019
Su Y-H, Li W-T, Sun H-R: Positive solutions of singular -Laplacian BVPs with sign changing nonlinearity on time scales. Mathematical and Computer Modelling 2008,48(5–6):845–858. 10.1016/j.mcm.2007.11.008
Sun H-R, Li W-T: Existence theory for positive solutions to one-dimensional -Laplacian boundary value problems on time scales. Journal of Differential Equations 2007,240(2):217–248. 10.1016/j.jde.2007.06.004
Zhou CL, Ma DX: Existence and iteration of positive solutions for a generalized right-focal boundary value problem with -Laplacian operator. Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications 2006,324(1):409–424. 10.1016/j.jmaa.2005.10.086
Anderson DR, Cabada A: Third-order right-focal multi-point problems on time scales. Journal of Difference Equations and Applications 2006,12(9):919–935. 10.1080/10236190600839322
Han W, Kang S: Multiple positive solutions of nonlinear third-order BVP for a class of -Laplacian dynamic equations on time scales. Mathematical and Computer Modelling 2009,49(3–4):527–535. 10.1016/j.mcm.2008.08.002
Deimling K: Nonlinear Functional Analysis. Springer, Berlin, Germany; 1985:xiv+450.
Guo DJ, Lakshmikantham V: Nonlinear Problems in Abstract Cones, Notes and Reports in Mathematics in Science and Engineering. Volume 5. Academic Press, Boston, Mass, USA; 1988:viii+275.
Avery RI, Peterson AC: Three positive fixed points of nonlinear operators on ordered Banach spaces. Computers & Mathematics with Applications 2001,42(3–5):313–322.
Acknowledgment
Supported by the NNSF of China (10801065) and NSF of Gansu Province of China (0803RJZA096).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 2.0 International License ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0 ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Bian, LH., He, XP. & Sun, HR. Multiple Positive Solutions of  -Point BVPs for Third-Order
-Point BVPs for Third-Order  -Laplacian Dynamic Equations on Time Scales.
Adv Differ Equ 2009, 262857 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1155/2009/262857
-Laplacian Dynamic Equations on Time Scales.
Adv Differ Equ 2009, 262857 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1155/2009/262857
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2009/262857
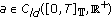 and
and 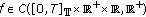 , both
, both  and
and 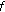 do not vanish identically on any closed subinterval of
do not vanish identically on any closed subinterval of  , and there exists
, and there exists 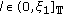 such that
such that 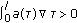 hold;
hold;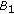 and
and 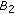 satisfying
satisfying  for
for 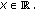
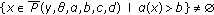 and
and 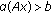 for
for  ;
; for
for 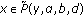 with
with 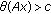 ;
;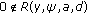 and
and  for
for 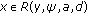 with
with 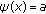 .
.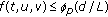 for
for 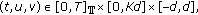
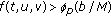 for
for 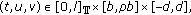
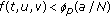 for
for 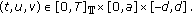
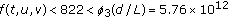 for
for 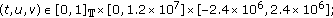
 for
for 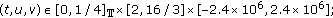
 for
for