- Research Article
- Open access
- Published:
On Boundedness of Solutions of the Difference Equation 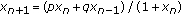 for
for 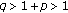
Advances in Difference Equations volume 2009, Article number: 463169 (2009)
Abstract
We study the boundedness of the difference equation  ,
,  where
where  and the initial values
and the initial values  . We show that the solution
. We show that the solution  of this equation converges to
of this equation converges to  if
if  or
or  for all
for all  ; otherwise
; otherwise  is unbounded. Besides, we obtain the set of all initial values
is unbounded. Besides, we obtain the set of all initial values  such that the positive solutions
such that the positive solutions  of this equation are bounded, which answers the open problem 6.10.12 proposed by Kulenović and Ladas (2002).
of this equation are bounded, which answers the open problem 6.10.12 proposed by Kulenović and Ladas (2002).
1. Introduction
In this paper, we study the following difference equation:

where  with
with  and the initial values
and the initial values  .
.
The global behavior of (1.1) for the case  is certainly folklore. It can be found, for example, in [1] (see also a precise result in [2,]).
is certainly folklore. It can be found, for example, in [1] (see also a precise result in [2,]).
The global stability of (1.1) for the case  follows from the main result in [3] (see also Lemma 1 in Stević's paper [4]). Some generalizations of Copson's result can be found, for example, in papers [5–8]. Some more sophisticated results, such as finding the asymptotic behavior of solutions of (1.1) for the case
follows from the main result in [3] (see also Lemma 1 in Stević's paper [4]). Some generalizations of Copson's result can be found, for example, in papers [5–8]. Some more sophisticated results, such as finding the asymptotic behavior of solutions of (1.1) for the case  (even when
(even when  ) can be found, for example, in papers [4](see also [8–11]). Some other properties of (1.1) have been also treated in [4].
) can be found, for example, in papers [4](see also [8–11]). Some other properties of (1.1) have been also treated in [4].
The case  was treated for the first time by Stević's in paper [12]. The main trick from [12] has been later used with a success for many times; see, for example, [13–15].
was treated for the first time by Stević's in paper [12]. The main trick from [12] has been later used with a success for many times; see, for example, [13–15].
Some existing results for (1.1) are summarized as follows[16].
Theorem 1 A.
 If
If  , then the zero equilibrium of (1.1) is globally asymptotically stable.
, then the zero equilibrium of (1.1) is globally asymptotically stable.
 If
If  , then the equilibrium
, then the equilibrium  of (1.1) is globally asymptotically stable.
of (1.1) is globally asymptotically stable.
 If
If  , then every positive solution of (1.1) converges to the positive equilibrium
, then every positive solution of (1.1) converges to the positive equilibrium  .
.
 If
If  , then every positive solution of (1.1) converges to a period-two solution.
, then every positive solution of (1.1) converges to a period-two solution.
 If
If  , then (1.1) has unbounded solutions.
, then (1.1) has unbounded solutions.
In [16], Kulenović and Ladas proposed the following open problem.
Open problem B (see Open problem 6.10.12of [16])
Assume that  .
.
-
(a)
Find the set
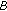 of all initial conditions
of all initial conditions 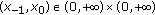 such that the solutions
such that the solutions 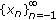 of (1.1) are bounded.
of (1.1) are bounded. -
(b)
Let
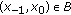 . Investigate the asymptotic behavior of
. Investigate the asymptotic behavior of 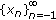 .
.
In this paper, we will obtain the following results: let  with
with  , and let
, and let  be a positive solution of (1.1) with the initial values
be a positive solution of (1.1) with the initial values  . If
. If  for all
for all  (or
(or  for all
for all  ), then
), then  converges to
converges to  . Otherwise
. Otherwise  is unbounded.
is unbounded.
2. Some Definitions and Lemmas
In this section, let  and
and  be the positive equilibrium of (1.1). Write
be the positive equilibrium of (1.1). Write  and define
and define  by, for all
by, for all  ,
,

It is easy to see that if  is a solution of (1.1), then
is a solution of (1.1), then  for any
for any  . Let
. Let

Then  . The proof of Lemma 2.1 is quite similar to that of Lemma 1 in [35] and hence is omitted.
. The proof of Lemma 2.1 is quite similar to that of Lemma 1 in [35] and hence is omitted.
Lemma 2.1.
The following statements are true.
-
(1)
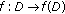 is a homeomorphism.
is a homeomorphism. -
(2)
 and
and  .
. -
(3)
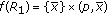 and
and 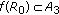 .
. -
(4)
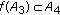 and
and  .
. -
(5)
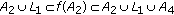 and
and  .
.
Lemma 2.2.
Let  , and let
, and let  be a positive solution of (1.1).
be a positive solution of (1.1).
-
(1)
If
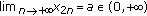 and
and  , then
, then 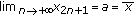 .
. -
(2)
If
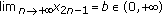 and
and 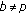 , then
, then  .
.
Proof.
We show only (1) because the proof of (2) follows from (1) by using the change  and the fact that (1) is autonomous. Since
and the fact that (1) is autonomous. Since  and
and  , by (1.1) we have
, by (1.1) we have

Also it follows from (1.1) that

from which we have  and
and  . This completes the proof.
. This completes the proof.
Lemma 2.3.
Let  , and let
, and let  be a positive solution of (1.1) with the initial values
be a positive solution of (1.1) with the initial values  . If there exists some
. If there exists some  such that
such that  , then
, then  .
.
Proof.
Since  , it follows from Lemma 2.1 that
, it follows from Lemma 2.1 that  for any
for any  . Without loss of generality we may assume that
. Without loss of generality we may assume that  , that is,
, that is,  . Now we show
. Now we show  Suppose for the sake of contradiction that
Suppose for the sake of contradiction that  , then
, then


By (2.5) we have

and by (2.6) we get

Claim 1.
If  , then
, then

Proof of Claim 1
Let  , then we have
, then we have

Since  , it follows
, it follows

This completes the proof of Claim 1.
By (2.8), we have

or

Claim 2.
We have


Proof of Claim 2
Since

we have

The proof of (2.14) is completed.
Now we show (2.15). Let

Note that  ; it follows that if
; it follows that if  , then
, then

which implies that  is decreasing for
is decreasing for  . Since
. Since  and
and

it follows that

Thus

This implies that

Finally we have

The proof of (2.15) is completed.
Note that  since
since  . By (2.12), (2.13), (2.14), and (2.15), we see
. By (2.12), (2.13), (2.14), and (2.15), we see  which contradicts to (2.7). The proof of Lemma 2.3 is completed.
which contradicts to (2.7). The proof of Lemma 2.3 is completed.
3. Main Results
In this section, we investigate the boundedness of solutions of (1.1). Let  , and let
, and let  be a positive solution of (1.1) with the initial values
be a positive solution of (1.1) with the initial values  , then we see that
, then we see that  for some
for some  or
or  for all
for all  or
or  for all
for all  .
.
Theorem 3.1.
Let  , and let
, and let  be a positive solution of (1.1) such that
be a positive solution of (1.1) such that  for all
for all  or
or  for all
for all  , then
, then  converges to
converges to  .
.
Proof.
Case 1.
 for any
for any  . If
. If  for some
for some  , then
, then

If  for some
for some  , then
, then

which implies that  and
and

Thus  for any
for any  . In similar fashion, we can show
. In similar fashion, we can show  for any
for any  . Let
. Let  and
and  , then
, then

which implies  .
.
Case 2.
 for any
for any  . Since
. Since  is decreasing in
is decreasing in  , it follows that for any
, it follows that for any 

In similar fashion, we can show that  . This completes the proof.
. This completes the proof.
Lemma 3.2 (see [20, Theorem 5]).
Let  be a set, and let
be a set, and let  be a function
be a function  which decreases in
which decreases in  and increases in
and increases in  , then for every positive solution
, then for every positive solution  of equation
of equation  ,
,  and
and  do exactly one of the following.
do exactly one of the following.
-
(1)
They are both monotonically increasing.
-
(2)
They are both monotonically decreasing.
-
(3)
Eventually, one of them is monotonically increasing, and the other is monotonically decreasing.
Remark 3.3.
Using arguments similar to ones in the proof of Lemma 3.2, Stevi proved Theorem 2 in [25]. Beside this, this trick have been used by Stević in [18, 28, 29].
proved Theorem 2 in [25]. Beside this, this trick have been used by Stević in [18, 28, 29].
Theorem 3.4.
Let  , and let
, and let  be a positive solution of (1.1) such that
be a positive solution of (1.1) such that  for some
for some  , then
, then  is unbounded.
is unbounded.
Proof.
We may assume without loss of generality that  and
and  (the proof for
(the proof for  is similar). From Lemma 2.1 we see
is similar). From Lemma 2.1 we see  for all
for all  .If
.If  is eventually increasing, then it follows from Lemma 2.3 that
is eventually increasing, then it follows from Lemma 2.3 that  is eventually increasing. Thus
is eventually increasing. Thus  and
and  , it follows from Lemma 2.2 that
, it follows from Lemma 2.2 that  .
.
If  is not eventually increasing, then there exists some
is not eventually increasing, then there exists some  such that
such that

from which we obtain  , since
, since  and
and  .
.
Since  is increasing in
is increasing in  and is decreasing in
and is decreasing in  , we have that
, we have that  for any
for any  . It follows from Lemma 3.2 that
. It follows from Lemma 3.2 that  is eventually decreasing. Thus
is eventually decreasing. Thus  and
and  . It follows from Lemma 2.2 that
. It follows from Lemma 2.2 that  . This completes the proof.
. This completes the proof.
By Theorems 3.1 and 3.4 we have the following.
Corollary 3.5.
Let  , and let
, and let  be a positive bounded solution of (1.1), then
be a positive bounded solution of (1.1), then  for all
for all  or
or  for all
for all  .
.
Now one can find out the set of all initial values  such that the positive solutions of (1.1) are bounded. Let
such that the positive solutions of (1.1) are bounded. Let  For any
For any  let
let

It follows from Lemma 2.1 that  , which implies
, which implies

for any  .
.
Let  be the set of all initial values
be the set of all initial values  such that the positive solutions
such that the positive solutions  of (1.1) are bounded. Then we have the following theorem.
of (1.1) are bounded. Then we have the following theorem.
Theorem 3.6.
 .
.
Proof.
Let  be a positive solution of (1.1) with the initial values
be a positive solution of (1.1) with the initial values  .
.
If  , then
, then  for any
for any  , which implies
, which implies  for any
for any  . It follows from Theorem 3.1 that
. It follows from Theorem 3.1 that  .
.
If  , then
, then  , which implies
, which implies  for any
for any  . It follows from Theorem 3.1 that
. It follows from Theorem 3.1 that  .
.
Now assume that  is a positive solution of (1.1) with the initial values
is a positive solution of (1.1) with the initial values  .
.
If  , then it follows from Lemma 2.1 that
, then it follows from Lemma 2.1 that  , which along with Theorem 3.4 implies that
, which along with Theorem 3.4 implies that  is unbounded.
is unbounded.
If  , then there exists
, then there exists  such that
such that  . Thus
. Thus  . By Lemma 2.1, we obtain
. By Lemma 2.1, we obtain  and
and  , which along with Theorem 3.4 implies that
, which along with Theorem 3.4 implies that  is unbounded.
is unbounded.
If  , then there exists
, then there exists  such that
such that  and
and  . Again by Lemma 2.1 and Theorem 3.4, we have that
. Again by Lemma 2.1 and Theorem 3.4, we have that  is unbounded. This completes the proof.
is unbounded. This completes the proof.
References
Tasković MR: Nonlinear Functional Analysis. Vol. I: Fundamental Elements of Theory. Zavod, za udžbenike i nastavna sredstva, Beograd, Serbia; 1993.
Stević S: Behavior of the positive solutions of the generalized Beddington-Holt equation. PanAmerican Mathematical Journal 2000,10(4):77-85.
Copson ET: On a generalisation of monotonic sequences. Proceedings of the Edinburgh Mathematical Society. Series 2 1970, 17: 159-164. 10.1017/S0013091500009433
Stević S: Asymptotic behavior of a sequence defined by iteration with applications. Colloquium Mathematicum 2002,93(2):267-276. 10.4064/cm93-2-6
Stević S: A note on bounded sequences satisfying linear inequalities. Indian Journal of Mathematics 2001,43(2):223-230.
Stević S: A generalization of the Copson's theorem concerning sequences which satisfy a linear inequality. Indian Journal of Mathematics 2001,43(3):277-282.
Stević S: A global convergence result. Indian Journal of Mathematics 2002,44(3):361-368.
Stević S:A note on the recursive sequence
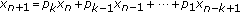 . Ukrainian Mathematical Journal 2003,55(4):691-697.
. Ukrainian Mathematical Journal 2003,55(4):691-697.Stević S:On the recursive sequence
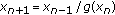 . Taiwanese Journal of Mathematics 2002,6(3):405-414.
. Taiwanese Journal of Mathematics 2002,6(3):405-414.Stević S: Asymptotics of some classes of higher-order difference equations. Discrete Dynamics in Nature and Society 2007, 2007:-20.
Stević S: Existence of nontrivial solutions of a rational difference equation. Applied Mathematics Letters 2007,20(1):28-31. 10.1016/j.aml.2006.03.002
Stević S:On the recursive sequence
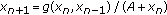 . Applied Mathematics Letters 2002, 15: 305-308. 10.1016/S0893-9659(01)00135-5
. Applied Mathematics Letters 2002, 15: 305-308. 10.1016/S0893-9659(01)00135-5Berenhaut KS, Dice JE, Foley JD, Iričanin B, Stević S:Periodic solutions of the rational difference equation
 . Journal of Difference Equations and Applications 2006,12(2):183-189. 10.1080/10236190500539295
. Journal of Difference Equations and Applications 2006,12(2):183-189. 10.1080/10236190500539295Stević S: Periodic character of a class of difference equation. Journal of Difference Equations and Applications 2004,10(6):615-619. 10.1080/10236190410001682103
Stević S:On the difference equation
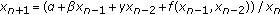 . Dynamics of Continuous, Discrete & Impulsive Systems 2007,14(3):459-463.
. Dynamics of Continuous, Discrete & Impulsive Systems 2007,14(3):459-463.Kulenović MRS, Ladas G: Dynamics of Second Order Rational Difference Equations, with Open Problems and Conjectures. Chapman & Hall/CRC Press, Boca Raton, Fla, USA; 2002:xii+218.
Amleh AM, Grove EA, Ladas G, Georgiou DA:On the recursive sequence
 . Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications 1999,233(2):790-798. 10.1006/jmaa.1999.6346
. Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications 1999,233(2):790-798. 10.1006/jmaa.1999.6346Berenhaut KS, Stević S:The behaviour of the positive solutions of the difference equation
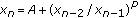 . Journal of Difference Equations and Applications 2006,12(9):909-918. 10.1080/10236190600836377
. Journal of Difference Equations and Applications 2006,12(9):909-918. 10.1080/10236190600836377Camouzis E, Ladas G: When does periodicity destroy boundedness in rational equations? Journal of Difference Equations and Applications 2006,12(9):961-979. 10.1080/10236190600822369
Camouzis E, Ladas G: When does local asymptotic stability imply global attractivity in rational equations? Journal of Difference Equations and Applications 2006,12(8):863-885. 10.1080/10236190600772663
Devault R, Kocic VL, Stutson D:Global behavior of solutions of the nonlinear difference equation
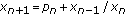 . Journal of Difference Equations and Applications 2005,11(8):707-719. 10.1080/10236190500137405
. Journal of Difference Equations and Applications 2005,11(8):707-719. 10.1080/10236190500137405Feuer J:On the behavior of solutions of
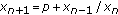 . Applicable Analysis 2004,83(6):599-606. 10.1080/00036810410001657260
. Applicable Analysis 2004,83(6):599-606. 10.1080/00036810410001657260Kulenović MRS, Ladas G, Prokup NR:On the recursive sequence
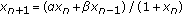 . Journal of Difference Equations and Applications 2000,6(5):563-576. 10.1080/10236190008808246
. Journal of Difference Equations and Applications 2000,6(5):563-576. 10.1080/10236190008808246Stević S: Asymptotic behavior of a nonlinear difference equation. Indian Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics 2003,34(12):1681-1687.
Stević S:On the recursive sequence
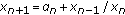 . II. Dynamics of Continuous, Discrete & Impulsive Systems. Series A 2003,10(6):911-916.
. II. Dynamics of Continuous, Discrete & Impulsive Systems. Series A 2003,10(6):911-916.Stević S:On the recursive sequence
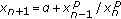 . Journal of Applied Mathematics & Computing 2005,18(1-2):229-234. 10.1007/BF02936567
. Journal of Applied Mathematics & Computing 2005,18(1-2):229-234. 10.1007/BF02936567Stević S:On the recursive sequence
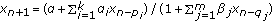 . Journal of Difference Equations and Applications 2007,13(1):41-46. 10.1080/10236190601069325
. Journal of Difference Equations and Applications 2007,13(1):41-46. 10.1080/10236190601069325Stević S:On the difference equation
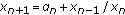 . Computers & Mathematics with Applications 2008,56(5):1159-1171. 10.1016/j.camwa.2008.02.017
. Computers & Mathematics with Applications 2008,56(5):1159-1171. 10.1016/j.camwa.2008.02.017Stević S, Berenhaut KS: The behavior of positive solutions of a nonlinear second-order difference equation. Abstract and Applied Analysis 2008, 2008:-8.
Sun T, Xi H: Global asymptotic stability of a family of difference equations. Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications 2005,309(2):724-728. 10.1016/j.jmaa.2004.11.040
Sun T, Xi H, Chen Z: Global asymptotic stability of a family of nonlinear recursive sequences. Journal of Difference Equations and Applications 2005,11(13):1165-1168. 10.1080/10236190500296516
Sun T, Xi H:On the system of rational difference equations
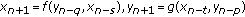 . Advances in Difference Equations 2006, 2006:-8.
. Advances in Difference Equations 2006, 2006:-8.Sun T, Xi H, Hong L:On the system of rational difference equations
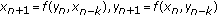 . Advances in Difference Equations 2006, 2006:-7.
. Advances in Difference Equations 2006, 2006:-7.Xi H, Sun T: Global behavior of a higher-order rational difference equation. Advances in Difference Equations 2006, 2006:-7.
Sun T, Xi H:On the basin of attraction of the two cycle of the difference equation
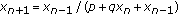 . Journal of Difference Equations and Applications 2007,13(10):945-952. 10.1080/10236190701388435
. Journal of Difference Equations and Applications 2007,13(10):945-952. 10.1080/10236190701388435
Acknowledgment
Project Supported by NNSF of China (10861002) and NSF of Guangxi (0640205, 0728002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 2.0 International License ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0 ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Xi, H., Sun, T., Yu, W. et al. On Boundedness of Solutions of the Difference Equation 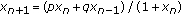 for
for 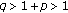 .
Adv Differ Equ 2009, 463169 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1155/2009/463169
.
Adv Differ Equ 2009, 463169 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1155/2009/463169
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2009/463169
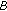 of all initial conditions
of all initial conditions 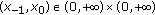 such that the solutions
such that the solutions 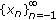 of (1.1) are bounded.
of (1.1) are bounded.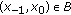 . Investigate the asymptotic behavior of
. Investigate the asymptotic behavior of 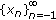 .
.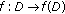 is a homeomorphism.
is a homeomorphism. and
and  .
.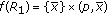 and
and 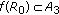 .
.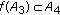 and
and  .
.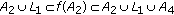 and
and  .
.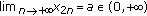 and
and  , then
, then 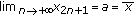 .
.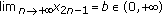 and
and 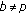 , then
, then  .
.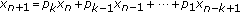 . Ukrainian Mathematical Journal 2003,55(4):691-697.
. Ukrainian Mathematical Journal 2003,55(4):691-697.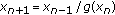 . Taiwanese Journal of Mathematics 2002,6(3):405-414.
. Taiwanese Journal of Mathematics 2002,6(3):405-414.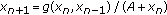 . Applied Mathematics Letters 2002, 15: 305-308. 10.1016/S0893-9659(01)00135-5
. Applied Mathematics Letters 2002, 15: 305-308. 10.1016/S0893-9659(01)00135-5 . Journal of Difference Equations and Applications 2006,12(2):183-189. 10.1080/10236190500539295
. Journal of Difference Equations and Applications 2006,12(2):183-189. 10.1080/10236190500539295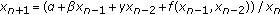 . Dynamics of Continuous, Discrete & Impulsive Systems 2007,14(3):459-463.
. Dynamics of Continuous, Discrete & Impulsive Systems 2007,14(3):459-463. . Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications 1999,233(2):790-798. 10.1006/jmaa.1999.6346
. Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications 1999,233(2):790-798. 10.1006/jmaa.1999.6346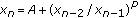 . Journal of Difference Equations and Applications 2006,12(9):909-918. 10.1080/10236190600836377
. Journal of Difference Equations and Applications 2006,12(9):909-918. 10.1080/10236190600836377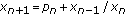 . Journal of Difference Equations and Applications 2005,11(8):707-719. 10.1080/10236190500137405
. Journal of Difference Equations and Applications 2005,11(8):707-719. 10.1080/10236190500137405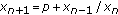 . Applicable Analysis 2004,83(6):599-606. 10.1080/00036810410001657260
. Applicable Analysis 2004,83(6):599-606. 10.1080/00036810410001657260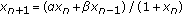 . Journal of Difference Equations and Applications 2000,6(5):563-576. 10.1080/10236190008808246
. Journal of Difference Equations and Applications 2000,6(5):563-576. 10.1080/10236190008808246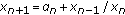 . II. Dynamics of Continuous, Discrete & Impulsive Systems. Series A 2003,10(6):911-916.
. II. Dynamics of Continuous, Discrete & Impulsive Systems. Series A 2003,10(6):911-916.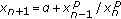 . Journal of Applied Mathematics & Computing 2005,18(1-2):229-234. 10.1007/BF02936567
. Journal of Applied Mathematics & Computing 2005,18(1-2):229-234. 10.1007/BF02936567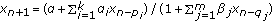 . Journal of Difference Equations and Applications 2007,13(1):41-46. 10.1080/10236190601069325
. Journal of Difference Equations and Applications 2007,13(1):41-46. 10.1080/10236190601069325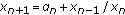 . Computers & Mathematics with Applications 2008,56(5):1159-1171. 10.1016/j.camwa.2008.02.017
. Computers & Mathematics with Applications 2008,56(5):1159-1171. 10.1016/j.camwa.2008.02.017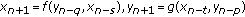 . Advances in Difference Equations 2006, 2006:-8.
. Advances in Difference Equations 2006, 2006:-8.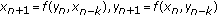 . Advances in Difference Equations 2006, 2006:-7.
. Advances in Difference Equations 2006, 2006:-7.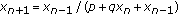 . Journal of Difference Equations and Applications 2007,13(10):945-952. 10.1080/10236190701388435
. Journal of Difference Equations and Applications 2007,13(10):945-952. 10.1080/10236190701388435