- Research
- Open access
- Published:
Qualitative behavior of a rational difference equation 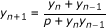
Advances in Difference Equations volume 2011, Article number: 6 (2011)
Abstract
This article is concerned with the following rational difference equation y n+1= (y n + y n-1)/(p + y n y n-1) with the initial conditions; y -1, y 0 are arbitrary positive real numbers, and p is positive constant. Locally asymptotical stability and global attractivity of the equilibrium point of the equation are investigated, and non-negative solution with prime period two cannot be found. Moreover, simulation is shown to support the results.
Introduction
Difference equations are applied in the field of biology, engineer, physics, and so on [1]. The study of properties of rational difference equations has been an area of intense interest in the recent years [6, 7]. There has been a lot of work deal with the qualitative behavior of rational difference equation. For example, Çinar [2] has got the solutions of the following difference equation:

Karatas et al. [3] gave that the solution of the difference equation:

In this article, we consider the qualitative behavior of rational difference equation:

with initial conditions y -1, y 0 ∈ (0, + ∞), p ∈ R +.
Preliminaries and notation
Let us introduce some basic definitions and some theorems that we need in what follows.
Lemma 1. Let I be some interval of real numbers and

be a continuously differentiable function. Then, for every set of initial conditions, x -k , x -k+1, ..., x 0 ∈ I the difference equation

has a unique solution  .
.
Definition 1 (Equilibrium point). A point  is called an equilibrium point of Equation 2, if
is called an equilibrium point of Equation 2, if

Definition 2 (Stability).
-
(1)
The equilibrium point
 of Equation 2 is locally stable if for every ε > 0, there exists δ > 0, such that for any initial data x
-k
, x
-k+1, ..., x
0 ∈ I, with
of Equation 2 is locally stable if for every ε > 0, there exists δ > 0, such that for any initial data x
-k
, x
-k+1, ..., x
0 ∈ I, with
we have
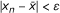 , for all n ≥ - k.
, for all n ≥ - k. -
(2)
The equilibrium point
 of Equation 2 is locally asymptotically stable if
of Equation 2 is locally asymptotically stable if  is locally stable solution of Equation 2, and there exists γ > 0, such that for all x
-k
, x
-k+1, ..., x
0 ∈ I, with
is locally stable solution of Equation 2, and there exists γ > 0, such that for all x
-k
, x
-k+1, ..., x
0 ∈ I, with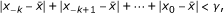
we have
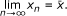
-
(3)
The equilibrium point
 of Equation 2 is a global attractor if for all x
-k
, x
-k+1, ..., x
0 ∈ I, we have
of Equation 2 is a global attractor if for all x
-k
, x
-k+1, ..., x
0 ∈ I, we have 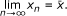 .
. -
(4)
The equilibrium point
 of Equation 2 is globally asymptotically stable if
of Equation 2 is globally asymptotically stable if  is locally stable and
is locally stable and  is also a global attractor of Equation 2.
is also a global attractor of Equation 2. -
(5)
The equilibrium point
 of Equation 2 is unstable if
of Equation 2 is unstable if  is not locally stable.
is not locally stable.
Definition 3 The linearized equation of (2) about the equilibrium  is the linear difference equation:
is the linear difference equation:

Lemma 2 [4]. Assume that p 1, p 2 ∈ R and k ∈ {1, 2, ...}, then

is a sufficient condition for the asymptotic stability of the difference equation

Moreover, suppose p 2 > 0, then, |p 1| + |p 2| < 1 is also a necessary condition for the asymptotic stability of Equation 4.
Lemma 3 [5]. Let g:[p, q]2 → [p, q] be a continuous function, where p and q are real numbers with p < q and consider the following equation:

Suppose that g satisfies the following conditions:
-
(1)
g(x, y) is non-decreasing in x ∈ [p, q] for each fixed y ∈ [p, q], and g(x, y) is non-increasing in y ∈ [p, q] for each fixed x ∈ [p, q].
-
(2)
If (m, M) is a solution of system
M = g(M, m) and m = g(m, M),
then M = m.
Then, there exists exactly one equilibrium  of Equation 5, and every solution of Equation 5 converges to
of Equation 5, and every solution of Equation 5 converges to  .
.
The main results and their proofs
In this section, we investigate the local stability character of the equilibrium point of Equation 1. Equation 1 has an equilibrium point

Let f:(0, ∞)2 → (0, ∞) be a function defined by

Therefore, it follows that

Theorem 1.
-
(1)
Assume that p > 2, then the equilibrium point
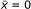 of Equation 1 is locally asymptotically stable.
of Equation 1 is locally asymptotically stable. -
(2)
Assume that 0 < p < 2, then the equilibrium point
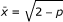 of Equation 1 is locally asymptotically stable, the equilibrium point
of Equation 1 is locally asymptotically stable, the equilibrium point 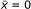 is unstable.
is unstable.
Proof. (1) when 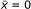 ,
,

The linearized equation of (1) about 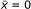 is
is

It follows by Lemma 2, Equation 7 is asymptotically stable, if p > 2.
(2) when 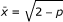 ,
,

The linearized equation of (1) about 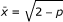 is
is

It follows by Lemma 2, Equation 8 is asymptotically stable, if

Therefore,

Equilibrium point 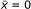 is unstable, it follows from Lemma 2. This completes the proof.
is unstable, it follows from Lemma 2. This completes the proof.
Theorem 2. Assume that  , the equilibrium point
, the equilibrium point 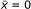 and
and 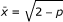 of Equation 1 is a global attractor.
of Equation 1 is a global attractor.
Proof. Let p, q be real numbers and assume that g:[p, q]2 → [p, q] be a function defined by  , then we can easily see that the function g(u, v) increasing in u and decreasing in v.
, then we can easily see that the function g(u, v) increasing in u and decreasing in v.
Suppose that (m, M) is a solution of system
M = g(M, m) and m = g(m, M).
Then, from Equation 1

Therefore,


Subtracting Equation 10 from Equation 9 gives

Since p+Mm ≠ 0, it follows that

Lemma 3 suggests that  is a global attractor of Equation 1 and then, the proof is completed.
is a global attractor of Equation 1 and then, the proof is completed.
Theorem 3. (1) has no non-negative solution with prime period two for all p ∈ R +.
Proof. Assume for the sake of contradiction that there exist distinctive non-negative real numbers φ and ψ, such that

is a prime period-two solution of (1).
φ and ψ satisfy the system


Subtracting Equation 11 from Equation 12 gives

so φ = ψ, which contradicts the hypothesis φ ≠ ψ. The proof is complete.
Numerical simulation
In this section, we give some numerical simulations to support our theoretical analysis. For example, we consider the equation:



We can present the numerical solutions of Equations 13-15 which are shown, respectively in Figures 1, 2 and 3. Figure 1 shows the equilibrium point  of Equation 13 is locally asymptotically stable with initial data x
0 = 1, x
1 = 1.2. Figure 2 shows the equilibrium point
of Equation 13 is locally asymptotically stable with initial data x
0 = 1, x
1 = 1.2. Figure 2 shows the equilibrium point  of Equation 14 is locally asymptotically stable with initial data x
0 = 1, x
1 = 1.2. Figure 3 shows the equilibrium point
of Equation 14 is locally asymptotically stable with initial data x
0 = 1, x
1 = 1.2. Figure 3 shows the equilibrium point 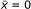 of Equation 15 is locally asymptotically stable with initial data x
0 = 1, x
1 = 1.2.
of Equation 15 is locally asymptotically stable with initial data x
0 = 1, x
1 = 1.2.
References
Berezansky L, Braverman E, Liz E: Sufficient conditions for the global stability of nonautonomous higher order difference equations. J Diff Equ Appl 2005,11(9):785-798. 10.1080/10236190500141050
Çinar C: On the positive solutions of the difference equation x n+1 = ax n-1 /1+ bx n x n-1 . Appl Math Comput 2004,158(3):809-812. 10.1016/j.amc.2003.08.140
Karatas R, Cinar C, Simsek D: On positive solutions of the difference equation x n+1 = x n-5 /1+ x n-2 x n-5 . Int J Contemp Math Sci 2006,1(10):495-500.
Li W-T, Sun H-R: Global attractivity in a rational recursive sequence. Dyn Syst Appl 2002,3(11):339-345.
Kulenovic MRS, Ladas G: Dynamics of Second Order Rational Difference Equations with Open Problems and Conjectures. Chapman & Hall/CRC Press; 2001.
Elabbasy EM, El-Metwally H, Elsayed EM: On the difference equation x n+1 = ax n - bx n /( cx n - dx n-1 ). Adv Diff Equ 2006, 1-10.
Memarbashi R: Sufficient conditions for the exponential stability of nonautonomous difference equations. Appl Math Lett 2008,3(21):232-235.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors' contributions
Xiao Qian carried out the theoretical proof and drafted the manuscript. Shi Qi-hong participated in the design and coordination. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 2.0 International License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Qian, X., Qi-hong, S. Qualitative behavior of a rational difference equation 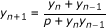 .
Adv Differ Equ 2011, 6 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1186/1687-1847-2011-6
.
Adv Differ Equ 2011, 6 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1186/1687-1847-2011-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1687-1847-2011-6

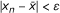 , for all n ≥ - k.
, for all n ≥ - k.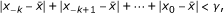
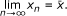

 , where x
0 = 1, x
1 = 1.2
, where x
0 = 1, x
1 = 1.2
 , where x
0 = 1, x
1 = 1.2
, where x
0 = 1, x
1 = 1.2
 , where x
0 = 1, x
1 = 1.2
, where x
0 = 1, x
1 = 1.2